- jvisualvm线程状态颜色
- 监视状态
- 等待状态
- 休眠状态
- Join
- 驻留状态
- 读取 IO
Java 线程状态
Java装状态流转如下
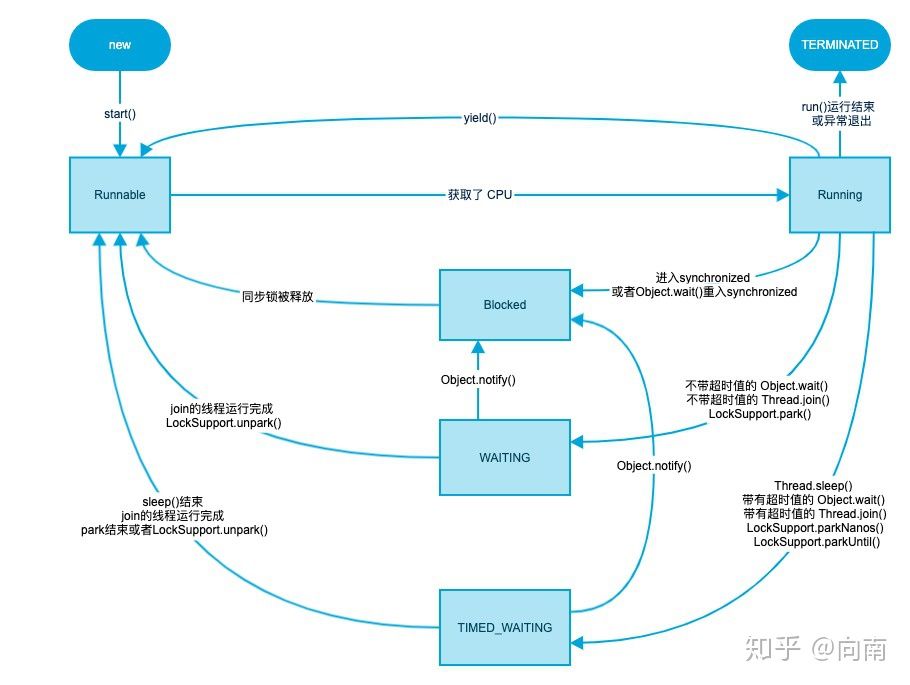
Running这个状态在Java平台中其实是不存在的,图中表示的只是获取了CPU的RUNNABLE状态。上图只是给出了一个大概的流程运转图,图里的有些操作是需要多个线程配合才能完成的,具体的流转过程在下面有详细的解释
Java线程状态在java.lang.Thread.State 这个枚举类中有描述
NEW:表示还未开始执行的状态RUNNABLE:表示线程是可运行,但目前等待系统运行资源(例如CPU等)BLOCKED:表示线程目前正在等待monitor lock,被阻塞住了。这种状态下是处于进入synchronized block/method 或者 调用Object.wait()之后重新进入 synchronized block/method 。WAITING:线程A处于等待操作,等待线程B执行一个特定的操作。当线程A调用了Object.wait()/ Thread.join()/ LockSupport.park() 这些方法后就会进入 WAITING状态TIMED_WAITING:线程处于一个带有超时时间的 WAITING 状态。当线程A调用了 Thread.sleep()/ Object.wait()/ Thread.join()/ LockSupport.parkNanos()/ LockSupport.parkUntil() 这些方法后就会进入 TIMED_WAITING 状态。TERMINATED: 表示线程执行完成了。
Java线程的状态不多,主要的也就是 BLOCKED/WAITING/TIMED_WAITING 这三个状态。
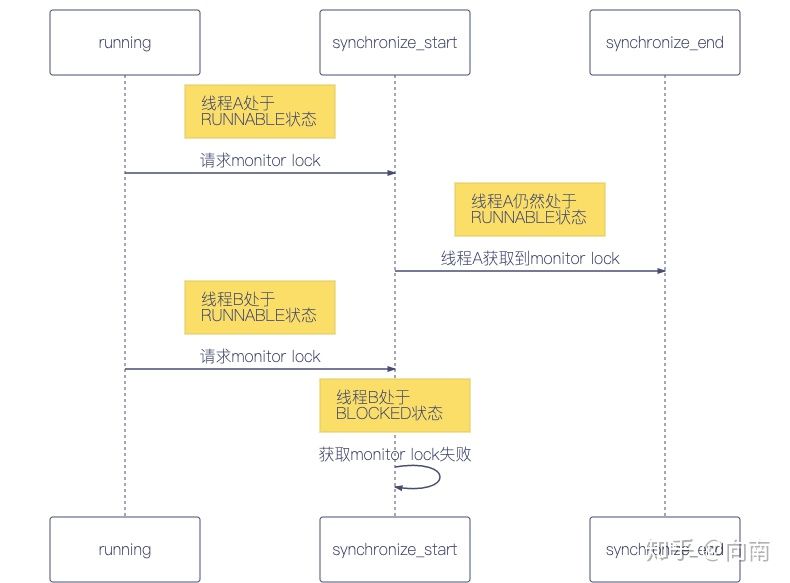
假设我们现在有AB俩个线程,刚开始这俩个线程都是处于RUNNABLE状态,假设都是运行状态(具体是否在运行取决于CPU调度)。然后俩个线程都要进入一段同步代码块,A成功获取到了监视锁,它进入了代码块继续处于RUNNABLE状态等待CPU调度。但是B获取监视锁失败了,于是就进入了BLOCKED状态,等待A释放监视锁。
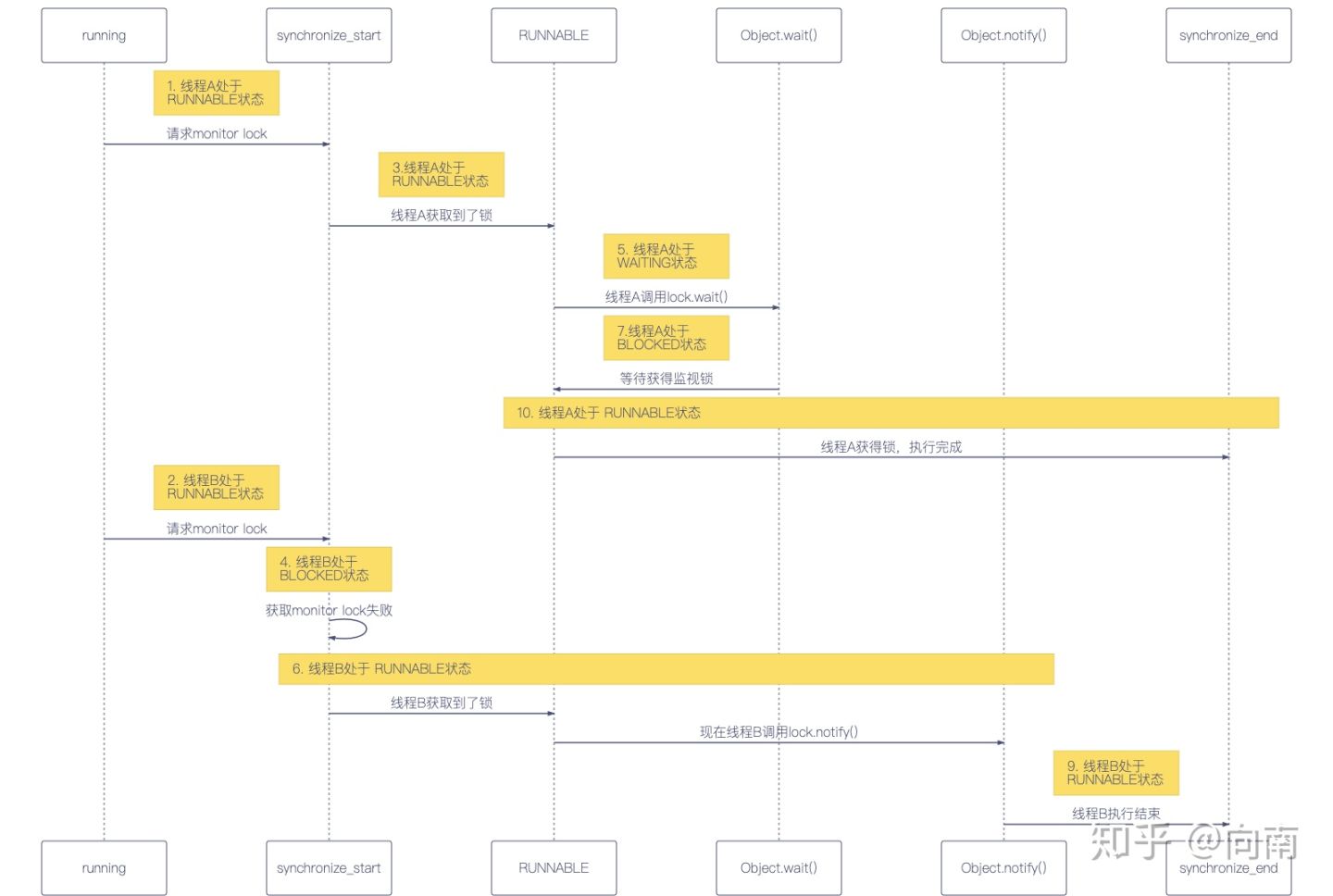
如果我们让A在同步块中执行监视锁对象的wait() 方法,A就会进入WAITING状态,释放监视锁等待B唤醒。B获得锁进入同步块后,调用监视锁对象的notify()方法唤醒A,此时A应该有一个短暂的RUNNABLE状态,然后进入进入BLOCKED状态等待B释放锁。
上面是Java里面定义的线程的状态, 那该状态是怎么来的呢?在源码中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public State java.lang.Thread.getState() {
return sun.misc.VM.toThreadState(threadStatus);
}
public static Thread.State sun.misc.VM.toThreadState(int threadStatus) {
if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_RUNNABLE) != 0) {
return RUNNABLE;
} else if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_BLOCKED_ON_MONITOR_ENTER) != 0) {
return BLOCKED;
} else if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_INDEFINITELY) != 0) {
return WAITING;
} else if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_WITH_TIMEOUT) != 0) {
return TIMED_WAITING;
} else if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_TERMINATED) != 0) {
return TERMINATED;
} else if ((threadStatus & JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE) == 0) {
return NEW;
} else {
return RUNNABLE;
}
}
|
我们发现java.lang.Thread.State是java.lang.Thread#threadStatus与JVMTI_THREAD_STATE 进行与计算得来的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| enum ThreadStatus {
NEW = 0,
RUNNABLE = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_RUNNABLE,
SLEEPING = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_WITH_TIMEOUT +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_SLEEPING,
IN_OBJECT_WAIT = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_INDEFINITELY +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_IN_OBJECT_WAIT,
IN_OBJECT_WAIT_TIMED = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_WITH_TIMEOUT +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_IN_OBJECT_WAIT,
PARKED = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_INDEFINITELY +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_PARKED,
PARKED_TIMED = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_WITH_TIMEOUT +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_PARKED,
BLOCKED_ON_MONITOR_ENTER = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE +
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_BLOCKED_ON_MONITOR_ENTER,
TERMINATED = JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_TERMINATED
};
enum {
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_ALIVE = 0x0001,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_TERMINATED = 0x0002,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_RUNNABLE = 0x0004,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_BLOCKED_ON_MONITOR_ENTER = 0x0400,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING = 0x0080,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_INDEFINITELY = 0x0010,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_WAITING_WITH_TIMEOUT = 0x0020,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_SLEEPING = 0x0040,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_IN_OBJECT_WAIT = 0x0100,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_PARKED = 0x0200,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_SUSPENDED = 0x100000,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_INTERRUPTED = 0x200000,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_IN_NATIVE = 0x400000,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_VENDOR_1 = 0x10000000,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_VENDOR_2 = 0x20000000,
JVMTI_THREAD_STATE_VENDOR_3 = 0x40000000
};
|
通过源码看java.lang.Thread中并没有对threadStatus 赋值的操作,那应该就是jvm赋值的
jvisualvm线程状态颜色
监视状态
进入锁 BLOCKED
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public class TestInSynchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);
Object lock = new Object();
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
Runnable runnable = () -> {
synchronized (lock) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int sec = atomicInteger.addAndGet(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running : " + sec + " seconds");
while ((System.currentTimeMillis() - start) < sec * 1000) {}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running finish");
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable, "Flying Thread");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable, "Running Thread");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread1);
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread2);
}
}
|
程序输出为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Flying Thread running : 2 seconds
Running Thread[BLOCKED] 1:-1
Flying Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
Flying Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
Running Thread[BLOCKED] 1:-1
Flying Thread running finish
Running Thread running : 4 seconds
Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 1:-1
Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 1:-1
Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 1:-1
Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 1:-1
Running Thread running finish
|
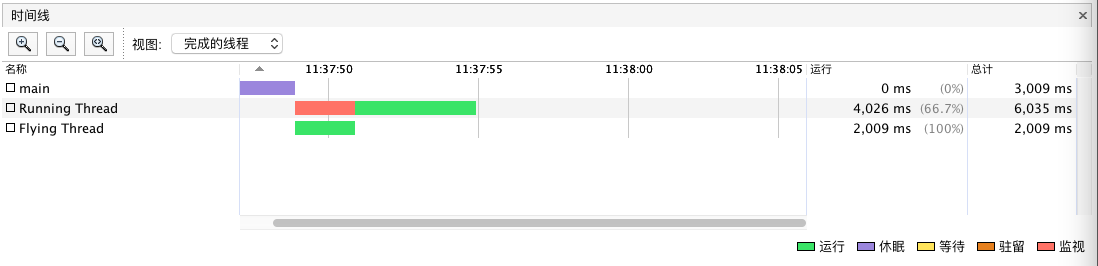
当线程进入锁之后,线程的状态就被切换成了监视状态。当线程运行完之后线程的颜色就变成了白色,表示运行完了
等待状态
调用wait() TIMED_WAITING
进入wait状态 调用Object.wait()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestThreadInWait {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);
final Object lock = new Object();
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
ThreadUtil.running(2);
synchronized (lock) {
try {
lock.wait(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
ThreadUtil.running(2);
}, "User");
thread.start();
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread);
}
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| 2017-09-28T12:16:19.669 User[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:20.646 User[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:21.646 User[TIMED_WAITING] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:22.647 User[TIMED_WAITING] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:23.647 User[TIMED_WAITING] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:24.647 User[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:25.647 User[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:16:26.644 User[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
|
当线程进入wait时, 并不是阻塞并不会计数,waitedCount一直在增长
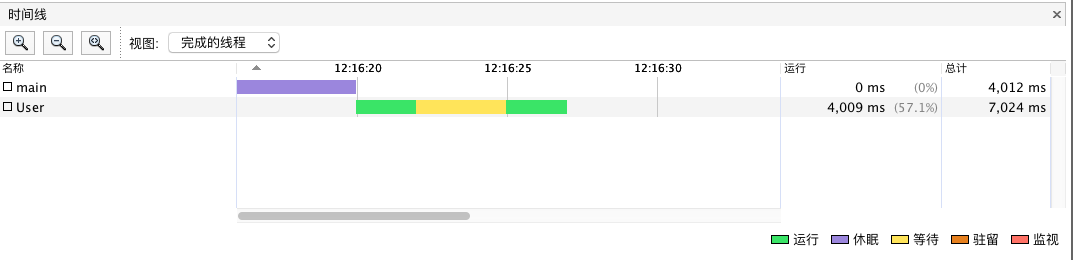
休眠状态
Thread.sleep() TIMED_WAITING
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestStateInSleep {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
ThreadUtil.running(2);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.running(1);
}, "User");
thread.start();
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread);
}
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
| 2017-09-28T12:13:23.309 User[RUNNABLE] 3:-1
2017-09-28T12:13:24.287 User[RUNNABLE] 3:-1
2017-09-28T12:13:25.287 User[TIMED_WAITING] 3:-1
2017-09-28T12:13:26.287 User[TIMED_WAITING] 3:-1
2017-09-28T12:13:27.288 User[RUNNABLE] 3:-1
|
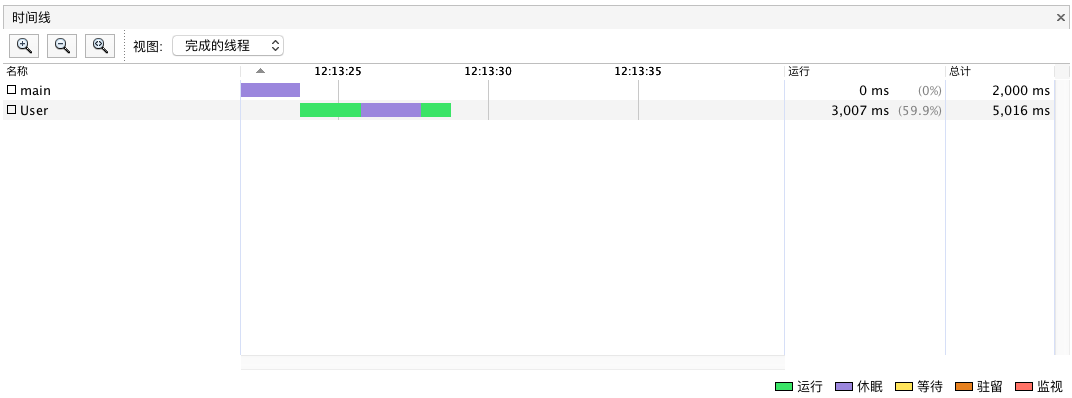
Join
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadJoin {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
ThreadUtil.running(2);
}, "User");
thread.start();
thread.join();
ThreadUtil.running(2);
}
}
|
驻留状态
WAITING
Java5 Lock
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TestInLock {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
Runnable runnable = () -> {
try {
lock.lock();
int sec = atomicInteger.addAndGet(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running : " + sec + " seconds");
ThreadUtil.running(sec);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running finish");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable, "Flying Thread");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable, "Running Thread");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread1);
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread2);
}
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Flying Thread running : 2 seconds
2017-09-28T12:29:33.728 Flying Thread[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:33.729 Running Thread[WAITING] 0:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:34.711 Flying Thread[RUNNABLE] 2:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:34.711 Running Thread[WAITING] 0:-1
Flying Thread running finish
Running Thread running : 4 seconds
2017-09-28T12:29:35.711 Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:36.709 Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:37.711 Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
2017-09-28T12:29:38.709 Running Thread[RUNNABLE] 0:-1
Running Thread running finish
|
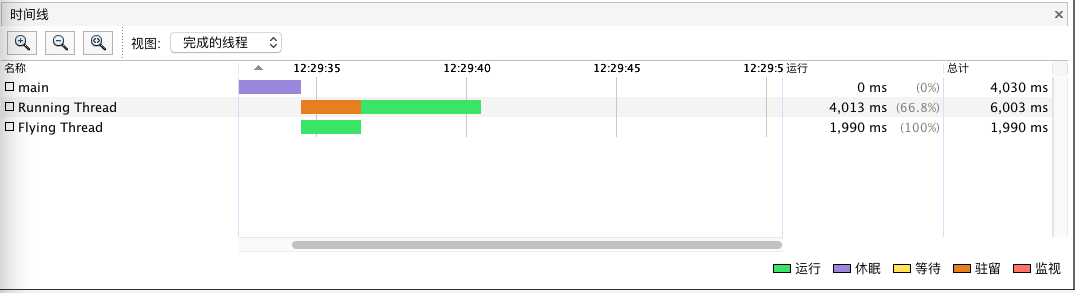
读取 IO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class TestIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);
Runnable runnable = () -> {
File file = new File("/Users/dawangyu/123.mkv");
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 1024];
fileInputStream.read(bytes);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable, "Flying Thread");
thread1.start();
ThreadUtil.printThreadState(thread1);
}
}
|
读取操作java thread 一直是运行状态










