第一步,构造JarLauncher 第二步,调用 launch() 方法
SpringBoot Loader 浅析
最近在写个小工具(jrc ),需要遍历springboot fat jar里的文件夹和文件,因为springboot fat jar 是利用SpringBoot Loader 进行加载的,所以花了一点时间研究一下这个框架。
相比于maven-jar-plugin打出的包, 用spring-boot-maven-plugin`` 打出的包多了一个BOOT-INF`文件夹,例如
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 ├── BOOT-INF │ ├── classes │ │ ├── application.properties │ │ ├── co │ │ │ └── wangming │ │ │ └── jrc │ │ │ └── jrcwebserver │ │ │ └── JrcWebServerApplication.class │ │ └── static │ └── lib │ ├── commons-io-2.6.jar ├── META-INF │ ├── MANIFEST.MF │ └── maven │ └── co.wangming.jrc │ └── jrc-web-server │ ├── pom.properties │ └── pom.xml └── org └── springframework └── boot └── loader ├── ExecutableArchiveLauncher.class ├── JarLauncher.class ├── LaunchedURLClassLoader.class ├── Launcher.class ├── MainMethodRunner.class ├── archive ├── data ├── jar └── util
很明显地可以看出BOOT-INF 这个路径里放的是我们的工程依赖(lib目录)和工程源码(classes目录)。
从META-INF/MANIFEST.MF 文件中我们可以看到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Manifest-Version: 1.0 Implementation-Title: jrc-web-server Implementation-Version: 0.1 Start-Class: co.wangming.jrc.jrcwebserver.JrcWebServerApplication Spring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/ Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/ Build-Jdk-Spec: 1.8 Spring-Boot-Version: 2.2.6.RELEASE Created-By: Maven Archiver 3.4.0 Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher
真正的启动类是 org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher。
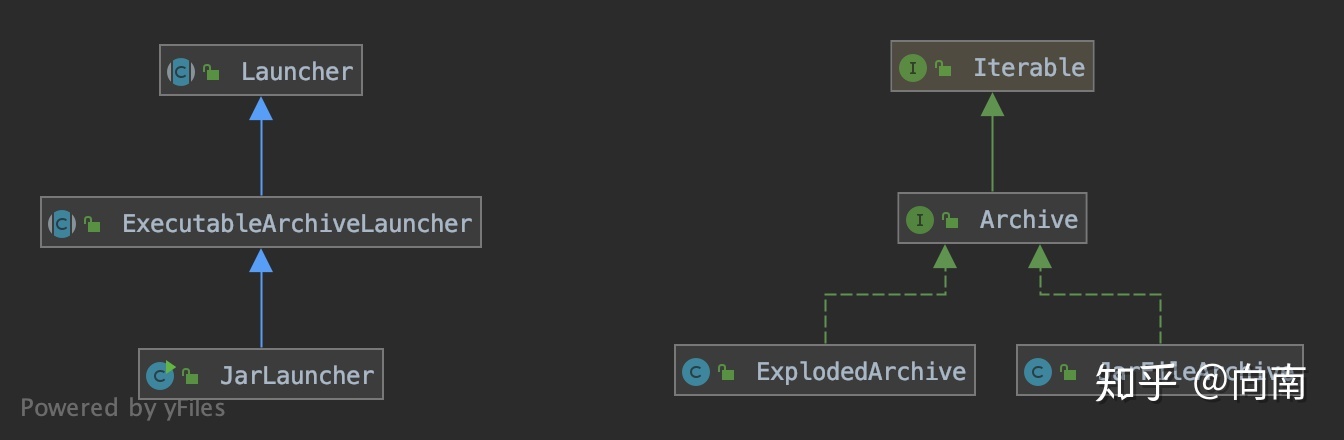
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher static final String BOOT_INF_CLASSES = "BOOT-INF/classes/" ; static final String BOOT_INF_LIB = "BOOT-INF/lib/" ; public JarLauncher () public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new JarLauncher().launch(args); } }
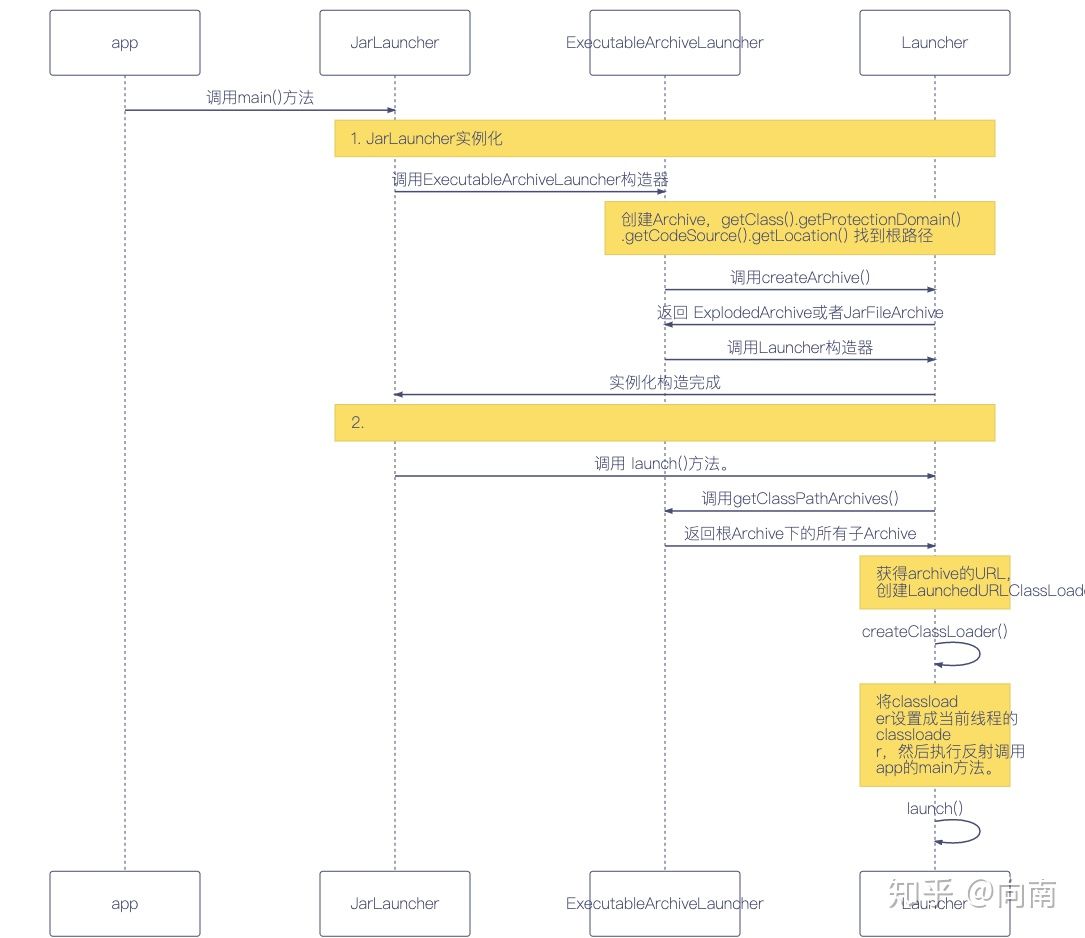
我针对这个启动流程画了一张时序图
结合刚才的源码和上面的时序图,启动过程分为俩步
构造 JarLauncher实例
调用launch(args) 方法,从而反射调用我们自己应用程序里的定义的main方法。
第一步,构造JarLauncher 这一步最重要的就是要把ExecutableArchiveLauncher 里的 Archive 构建出来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 protected final Archive createArchive () throws Exception ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getClass().getProtectionDomain(); CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource(); URI location = (codeSource != null ) ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null ; String path = (location != null ) ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null ; if (path == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive" ); } File root = new File(path); if (!root.exists()) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable to determine code source archive from " + root); } return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root)); }
上面这一段代码是在 Launcher 这个类里,所以 getClass().getProtectionDomain() 等同于 org.springframework.boot.loader.Launcher.class.getProtectionDomain() 最终获取到的path就是spring-boot-maven-plugin 打出的fat jar的绝对路径。
第二步,调用 launch() 方法 构建完Launcher之后,就开始进行第二步,调用 launch(args) 方法。
这个方法是定义在了org.springframework.boot.loader.Launcher里
1 2 3 4 5 protected void launch (String[] args) throws Exception JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler(); ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(getClassPathArchives()); launch(args, getMainClass(), classLoader); }
首先通过调用getClassPathArchives()获取到所有的Archive,然后将所有的Archive对应的URL取到,开始创建ClassLoader
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected ClassLoader createClassLoader (List<Archive> archives) throws Exception List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>(archives.size()); for (Archive archive : archives) { urls.add(archive.getUrl()); } return createClassLoader(urls.toArray(new URL[urls.size()])); } protected ClassLoader createClassLoader (URL[] urls) throws Exception return new LaunchedURLClassLoader(urls, getClass().getClassLoader()); }
这段代码很简单,关键就在于 getClassPathArchives() 这个方法和 LaunchedURLClassLoader 这个类加载器内部的实现。
我们先分析以getClassPathArchives()这个方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Override protected List<Archive> getClassPathArchives () throws Exception List<Archive> archives = new ArrayList<Archive>( this .archive.getNestedArchives(new EntryFilter() { @Override public boolean matches (Entry entry) return isNestedArchive(entry); } })); postProcessClassPathArchives(archives); return archives; } @Override protected boolean isNestedArchive (Archive.Entry entry) if (entry.isDirectory()) { return entry.getName().equals("BOOT-INF/classes/" ); } return entry.getName().startsWith("BOOT-INF/lib/" ); }
这段代码就是将根archive里面所有以BOOT-INF/classes/或者BOOT-INF/lib/开头的子archive都加载出来。
关键代码是Archive类的getNestedArchives()方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public List<Archive> getNestedArchives (EntryFilter filter) throws IOException List<Archive> nestedArchives = new ArrayList<Archive>(); for (Entry entry : this ) { if (filter.matches(entry)) { nestedArchives.add(getNestedArchive(entry)); } } return Collections.unmodifiableList(nestedArchives); } @Override public Iterator<Entry> iterator () return new EntryIterator(this .jarFile.entries()); }
Archive接口 继承自 java.lang.Iterable 接口,因此在getNestedArchives()方法中直接对自身进行遍历。而遍历的数据源是来自org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarFile 这个类,它继承自java.util.jar.JarFile这个类,并对其进行类重写。
这段代码也很简单就是对从jarFile加载出来的项目进行遍历,然后调用过滤器判断是否是 以BOOT-INF/classes/或者BOOT-INF/lib/开头,如果是就添加,不是就跳过。
到目前为止,SpringBoot Loader里的 Archive 和 Launcher 就说完了。
下面开始就是对org.springframework.boot.loader.jar.JarFile的分析了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class JarFile extends java .util .jar .JarFile private final RandomAccessDataFile rootFile; private final RandomAccessData data; private final JarFileType type; private URL url; private JarFileEntries entries; private SoftReference<Manifest> manifest; } private JarFile (RandomAccessDataFile rootFile, String pathFromRoot, RandomAccessData data, JarEntryFilter filter, JarFileType type) throws IOException { this .rootFile = rootFile; CentralDirectoryParser parser = new CentralDirectoryParser(); this .entries = parser.addVisitor(new JarFileEntries(this , filter)); parser.addVisitor(centralDirectoryVisitor()); this .data = parser.parse(data, filter == null ); this .type = type; }
在JarFile的实例化过程中已经完成了对jar文件的解析工作了。具体的解析过程这里就不再展开了。
至此,整个SpringBoot Loader 分析工作完成。
那如果要遍历springboot fat jar里面的文件要怎么办呢?我是重新把ExecutableArchiveLauncher 和 JarLauncher 重新组合了一下,重写出一个新类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 class SpringBootLauncher extends Launcher private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringBootLauncher.class); Map<String, SpringBootArchiveEntry> entryCache = new HashMap<>(); static final String BOOT_INF_CLASSES = "BOOT-INF/classes/" ; static final String BOOT_INF_LIB = "BOOT-INF/lib/" ; private final Archive archive; public SpringBootLauncher () try { this .archive = createJrcArchive(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } } private Archive createJrcArchive () throws Exception Class<?> launcherClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.loader.Launcher" ); ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = launcherClass.getProtectionDomain(); CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource(); URI location = (codeSource != null ) ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null ; String path = (location != null ) ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null ; if (path == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive" ); } File root = new File(path); if (!root.exists()) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive from " + root); } return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root)); } @Override protected String getMainClass () throws Exception Manifest manifest = this .archive.getManifest(); String mainClass = null ; if (manifest != null ) { mainClass = manifest.getMainAttributes().getValue("Start-Class" ); } if (mainClass == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException("No 'Start-Class' manifest archiveEntry specified in " + this ); } return mainClass; } @Override protected List<Archive> getClassPathArchives () throws Exception List<Archive> archives = new ArrayList<>(this .archive.getNestedArchives(this ::isNestedArchive)); postProcessClassPathArchives(archives); logger.info("entryCache.size : {}" , entryCache.size()); return archives; } protected void postProcessClassPathArchives (List<Archive> archives) throws Exception for (Archive archive : archives) { Iterator<Archive.Entry> ite = archive.iterator(); while (ite.hasNext()) { Archive.Entry archiveEntry = ite.next(); SpringBootArchiveEntry entryItem = new SpringBootArchiveEntry(); entryItem.archiveEntry = archiveEntry; entryItem.archive = archive; entryCache.put(archiveEntry.getName(), entryItem); } postProcessClassPathArchives(archive.getNestedArchives(this ::isNestedArchive)); } } public List<SpringBootArchiveEntry> getEntries (String path) List<SpringBootArchiveEntry> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (Map.Entry<String, SpringBootArchiveEntry> stringEntryItemEntry : entryCache.entrySet()) { if (stringEntryItemEntry.getKey().startsWith(path)) { list.add(stringEntryItemEntry.getValue()); } } return list; } protected boolean isNestedArchive (Archive.Entry entry) if (entry.isDirectory()) { return entry.getName().equals(BOOT_INF_CLASSES); } return entry.getName().startsWith(BOOT_INF_LIB); } @Override protected void launch (String[] args, String mainClass, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Exception Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader); } public void launch () throws Exception super .launch(new String[]{}); } }
在postProcessClassPathArchives(archives); 这个方法中将所有的entry都缓存了下来。方便后期我遍历或者查询使用
文章参考彻底透析SpringBoot jar可执行原理